What is molluscum contagiosum?
Molluscum Contagiousum, or MC, is a viral skin infection, which primarily affects children and young adults.
However, anyone can suffer from this condition, which is part of the family of viruses known as poxviruses.
MC is highly contagious and can be spread through skin to skin contact, through sharing towels or in a child’s case, sharing toys, hugging or playing with someone who is infected. It can also spread in water.
Those with illnesses that can weaken the immune systems are also at risk.
However, many people are resistant to this condition meaning that even if they are exposed to the virus they won’t develop it.
Once someone has molluscum contagiosum it can be spread from one part of the body to another by scratching or rubbing the bumps and then touching another part of the body.
What are the symptoms of Molluscum Contagiosum?
Usually the only symptom of Molluscum Contagiousum is small spots. These are firm, raised and blister like, but rarely painful. However, you may notice your child is itching as a result. The spots can form in small clusters on the arms, face, neck, hands and stomach area. In rarer cases you may also spot these on the palm of the hand or soles of the feet, inside the mouth or even the eyelids. You should expect the spots to last for around six to 12 months, although it can take a little bit more time for them to totally disappear.
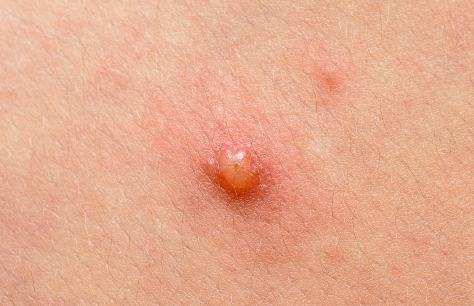
What are the treatments and remedies of Molluscum Contagiosum?
In many cases molluscum contagiosum is left to go away on its own without treatment.
If you can, try to discourage your child from touching, scratching, or rubbing the spots as this will make them worse and encourage them to spread.
Wash hands often with soap and water and keep areas with growths clean.
If your child is suffering with the condition or feeling particularly self-conscious then make an appointment with your GP who can, in some cases, prescribe an ointment to help speed up the healing process.
This guide
The information in this Bounty A-Z of Family Health is not a substitute for an examination, diagnosis or treatment by a doctor, midwife, health visitor or any other qualified health professional. If in doubt, always speak to a doctor.
Bounty will not be held responsible or liable for any injury, loss, damage, or illness, however this occurs or appears, after using the information given on this website and in particular the A-Z of Family Health.
Further help
For health advice and information 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, the NHS offers call and web services. You can also visit NHS websites for services, health information and health news at nhs.uk
- England – call 111 from any landline or mobile phone free of charge, or visit nhs.uk
- Scotland – call 111 from any landline or mobile phone free of charge, or visit nhs24.com
- Wales – call 0845 4647 , or visit nhsdirect.wales.nhs.uk
- Northern Ireland – visit hscni.net